
Compressed air systems are used in numerous industrial applications. These systems may include compressed air dryers and compressed air filters as well as gas generators depending on the need. For example, for production and applications in the medical field, water separators, compressed air line filters, dryers and oxygen generators are used respectively. One of the most widely used gas types industrially is nitrogen. Nitrogen gas has a wide supply-demand ratio and application area because it is colourless, odourless and especially inert (non-reactive). The purity of nitrogen gas significantly affects the final product quality in the application and the importance of nitrogen gas purity in the industry is the main subject of this article.
What are Nitrogen Gas Purity Ratios and How Are They Measured?
Atmospheric air is composed of various components, 78% Nitrogen (N2 ) and 21% Oxygen (O2 ) and 1% other gases. Because nitrogen and oxygen exist in high concentrations, the purity of nitrogen in a nitrogen (N₂) gas stream is usually expressed in ppm (parts per million) as a percentage of nitrogen relative to oxygen. For example, a nitrogen gas rated at 95 per cent purity is expressed as “containing 5 per cent oxygen (O₂)”. This means that in a sample of 95% pure nitrogen there may be 50,000 molecules of O₂ in 1 million molecules. Another way of expressing the 95% nitrogen purity level is to state that the nitrogen gas stream has an O₂ content of about 50,000 ppm and all the remaining proportion is the N2 components.

As nitrogen purity levels increase to 99.9% and above, it is more common for the purity of nitrogen to be specified in terms of the amount of O₂ remaining in the gas stream. For example, the O₂ content of a 99.9 per cent purity gas stream will be specified as 1,000 ppm. Similarly, the O₂ content of a 99.999% purity gas stream would be specified as 10 ppm. As the purity of nitrogen increases, it is a clearer measurement to state its purity in terms of the remaining O₂ content. There is also a convention in industrial gas use to specify the N₂ concentration as the total “9s” on either side of the decimal point of the purity percentage. For example, 99.9% N₂ purity would be referred to as a purity of 3-9, or a gas stream of 99.999% N₂ purity containing 10 ppm O₂ would be referred to as a gas purity of 5-9.
How is Nitrogen Gas Produced?
As nitrogen is highly abundant (78%) in the atmosphere, it is cost and practically advantageous for nitrogen gas users to invest in safer on-site, on-demand and instantaneous nitrogen production in their own facilities, rather than relying on cryogenic N₂ delivery. Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) or membrane production methods are generally used for the separation and enrichment of nitrogen from the atmosphere.
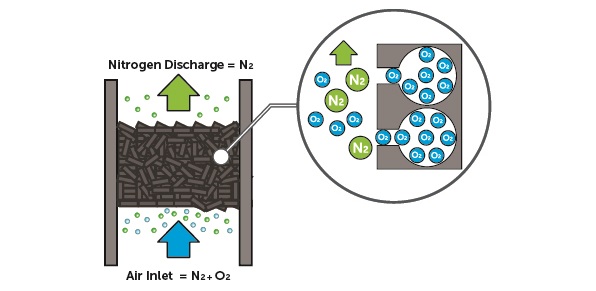
 PSA nitrogen production usually involves a carbon molecular sieve (CMS) adsorbent material filled tank and compressed air passed through this tank bed. O₂ molecules bind to the surface of the adsorbent material, predominantly its pores, and are retained until the desorption process. In this respect, the pore and material diameters of the adsorbent material are important. This process results in a nitrogen-enriched gas stream with N₂ purities ranging from 95% to 99.999%. When the adsorbent material is saturated with O₂, desorption occurs by depressurisation and O₂ molecules are released into the atmosphere. To ensure a continuous flow of nitrogen gas, PSA systems mostly utilise dual adsorption towers. While one tower produces N₂ gas, the other tower desorbs O₂ in preparation for the next process.
PSA nitrogen production usually involves a carbon molecular sieve (CMS) adsorbent material filled tank and compressed air passed through this tank bed. O₂ molecules bind to the surface of the adsorbent material, predominantly its pores, and are retained until the desorption process. In this respect, the pore and material diameters of the adsorbent material are important. This process results in a nitrogen-enriched gas stream with N₂ purities ranging from 95% to 99.999%. When the adsorbent material is saturated with O₂, desorption occurs by depressurisation and O₂ molecules are released into the atmosphere. To ensure a continuous flow of nitrogen gas, PSA systems mostly utilise dual adsorption towers. While one tower produces N₂ gas, the other tower desorbs O₂ in preparation for the next process.
Membrane technology is the process of passing compressed air through a membrane perforated with holes with microscopic pores. These pores allow smaller O₂ molecules and water vapour to pass through the hollow fibre structure and be discharged into the atmosphere, while larger N₂ molecules move across the membrane, providing a continuous flow of N₂ with purities ranging from 95% to 99.9%. With membrane technology, production with purities up to 99.9% can be achieved.
What are the industrial applications for Nitrogen Gas?
The importance of the amount of oxygen in nitrogen gas stems from the fact that, in many industrial production processes, the final product results and compressed air and filtration equipment are adversely affected by the presence of even very low oxygen concentrations. This is due to the fact that oxygen draws electrons from other elements and causes oxidation reactions. Oxygen is responsible for many of the undesirable oxidation reactions that occur in nature and industry, such as corrosion of metallic surfaces and degradation of organic matter (food and beverage industries). Therefore, in order to control the oxidation process in industrial applications, the oxygen content is either removed or reduced to such an oxygen-nitrogen ratio that the oxygen is not sufficient to produce harmful amounts of oxidation. For this, the importance of nitrogen gas in various industrial applications can be explained with a few examples:
Use of Nitrogen Gas in Food and Beverage Production Processes: Nitrogen gas is a colourless, odourless and tasteless gas found naturally in the atmosphere. It protects products from oxidation and extends shelf life by replacing oxygen in food and beverage production. The use of nitrogen gas is important in the production process of foods such as deli products, nuts, chips and liquids such as fruit juice, valuable oils, alcoholic beverages. Nitrogen Gas sent to the production lines from Mikropor MNG PRO series nitrogen generators creates a modified atmosphere and preserves the freshness of the products for a long time. Especially for foods such as milk and dairy products, dried nuts, coffee, wine, beer, whose smell and aroma are important for the consumer, the use of Nitrogen Gas is very important. Mikropor MNG PRO series nitrogen generator provides a cost-effective and safe gas source that can be used all day long for food and beverage production.
Nitrogen Gas Utilisation for Long Term Food Storage: Open or deformed packaged foods will spoil, as microbial growth will occur in the presence of oxygen. To eliminate oxidation of stored foods, the cold storage room is filled with nitrogen gas to reduce the oxygen concentration. Nitrogen purity levels between 95% and 99% allow foods to have a certain percentage longer shelf life in storage.
Use of Nitrogen Gas in Electronic Soldering Processes: In the electronics industry, many processors and critical products such as circuit boards are manufactured. Near-perfect soldering is required to join electrical components on circuit boards. The components are wetted with hot liquid metal (solder) and solidified after joining to form a durable bond. In this process, oxygen forms metal oxides with the solder, known as “dross”, which significantly affects the soldering process. Soldering in an environment with an oxygen concentration not exceeding 1000 ppm, i.e. 99.9% pure nitrogen gas, reduces dross formation, increases joint integrity and improves production quality by minimising the need for scrap or rework. Depending on the size of the brazing operation, the required volume of N₂ with a purity of 3-9% can be supplied on-site and easily with PSA technology.

 Nitrogen Gas Use in High Speed Laser Cutting: During the laser cutting process, O₂ in the atmosphere can oxidise the edges of the cut material, which can cause dulling or roughening of the material edges. After the cutting process, surface imperfections in the cut area can prevent the paint from being applied properly. For example, in order to obtain a glossy (non-dulled) result in cutting stainless steel 12mm or thicker, it is better to perform the cutting with high purity nitrogen and the purity range is 99.99% to 99.999% (4-9s and 5-9s). This means that the oxygen content should not be greater than 100 ppm to 10 ppm and the oxygen content should be limited. The faster the cutting speed, the higher the required nitrogen purity. N₂ supply for these applications can usually be realised economically by the PSA method, which can provide both the purity level and the required flow continuously.
Nitrogen Gas Use in High Speed Laser Cutting: During the laser cutting process, O₂ in the atmosphere can oxidise the edges of the cut material, which can cause dulling or roughening of the material edges. After the cutting process, surface imperfections in the cut area can prevent the paint from being applied properly. For example, in order to obtain a glossy (non-dulled) result in cutting stainless steel 12mm or thicker, it is better to perform the cutting with high purity nitrogen and the purity range is 99.99% to 99.999% (4-9s and 5-9s). This means that the oxygen content should not be greater than 100 ppm to 10 ppm and the oxygen content should be limited. The faster the cutting speed, the higher the required nitrogen purity. N₂ supply for these applications can usually be realised economically by the PSA method, which can provide both the purity level and the required flow continuously.
Nitrogen is a highly desireable gas for industrial and scientific applications because it is essential in the following situations:
- Prevent oxidation of materials
- Prevent microbial or bacterial growth
- Reducing the level of flammable gas
- Limiting the oxygen content and preventing it from reacting
In all these processes, nitrogen gas is used to reduce the oxygen concentration and eliminate or reduce the harmful effects of oxidation. The desired nitrogen purity may vary depending on the application. As a general application in production areas where industrial gas is used, nitrogen purity can be expressed as a percentage nitrogen content, as well as according to the oxygen impurity in it.
Mikropor PRO Series Nitrogen Generators
Mikropor branded PRO Series nitrogen generators offer high efficiency to industrial plants with their compact design and fully automatic operation. By eliminating the use of manifolds, it enables the system to operate more efficiently and safely. Thanks to the touchscreen PLC display, the entire system can be easily controlled and safe production is ensured with its fast start-up feature. Thanks to the new silencer, specially designed by Mikropor, it is possible to work with low noise levels during pressurisation and discharge processes. Durable piston valves provide long-lasting use and minimum maintenance requirements.
Mikropor MNG PRO Series Nitrogen Generators offer a low cost, high performance and energy efficient solution with nitrogen purity ranging from 95% to 99.999% according to customer requirements. It is one of the leading products in the industry with optimised air distribution and low air / nitrogen ratios in nitrogen gas production.
You can contact our expert sales teams to select the Mikropor MNG PRO Series Nitrogen Generator with the most suitable purity rate and capacity for your facility or to get more information, you can review our products here.
Mikropor R&D Department

